Bihar Board 12th Accountancy Important Questions Short Answer Type Part 2 in English
Bihar Board 12th Accountancy Important Questions Short Answer Type Part 2 in English
Question 1.
Explain the importance of partnership deed.
Answer:
The importance of partnership deed ate as follows :
- Helpful in smooth functioning of the business.
- Useful in resolve disputes and misunderstandings among partners.
- Useful in regulating the duties and responsibilities of each partner.
- If there is any dispute among the partners, the partnership deed will serve as an evidence in the court of law.
Question 2.
What do you mean by profit’& loss appropriation account?
Answer:
The net profit (after adjustment of partner’s transactions such as interests on capital, partner’s salary, commission drawings, interest on drawings etc.) is to be shared by all the partners in the agreed profit sharing ratio. For this purpose, a separate account is prepared for distribution of profits between j the partners, known as profit & loss appropriation account.
Question 3.
Explain the nature of goodwill.
Answer:
Like buildings, machinery and furniture etc. goodwill is also an asset, but the main point of difference is that building etc. can be seen and touched while goodwill cannot be seen and touched but felt, it is invisible hence it is treated as an intangible asset. All assets can be separately sold but goodwill cannot be separately sold. This is why, goodwill has no separate existence while other assets have. Hence, it is not a fictitious asset as it can be purchased or sold with any other asset.
Question 4.
What do you mean by retirement of a partner?
Answer:
A partner may wish to withdraw from a firm for various reasons like old age. Change of residence, on health ground, misunderstanding with other partners or any other reason. Such a situation is called retirement of a partner. So it means to leave the firm. Any such type of partner is known as retiring partner.
Question 5.
Give the meaning of death of a partner.
Answer:
When a partner dies, it means compulsory retirement and his representatives or the execution of his estate are entitled to all the rights. The representatives of the deceased partner will be entitled to his share of profit accrued upto the date of death.
Question 6.
What do you mean by dissolution of partnership firm?
Answer:
Dissolution of firm means discontinuance of economic relation between the partners. According to see 39 of Indian partnership act, 1932, “dissolution of firm means dissolution of partnership between all the partners in the firm.” When the complete business of the firm is closed down due to any reason, it is called dissolution of the firm.
Question 7.
What are the modes of dissolution of a partnership firm?
Answer:
The modes of dissolution of a partnership firm are as follows :
- Dissolution by agreement
- Compulsory dissolution
- Dissolution on the happening of certain contingency.
- Dissolution by notice Gn case of partnership at will.
- Dissolution by a court.
Question 8.
What do you mean by share of a company?
Answer:
The capital of a company is divided into a number of equal parts. Each part is called a share. A company many divide its capital into shares of 1, 2, 5, 10 or any suitable amounts (or denomination).
Question 9.
What is preference share?
Answer:
Preference share is on which carries the following two rights as per section 85 of companies act:
- They have a right to receive dividend at a fixed rate before any divided is paid on the equity shares.
- One the winding up of the company, they have right to return of capital before that of equity shares.
Question 10.
What is equity share?
Answer:
Under Indian companies act, 1956, “an equity share is a share which is not a preference share.” Thus, this share does not carry any preferential right. In other words, equity share is one which is entitled to dividend and repayment of capital after the claims of preference shares are satisfied.
Question 11.
Give the definition of debenture.
Answer:
According to sec. 2(12) of Indian companies act. 1956. “Debenture includes debenture stock, bonds and any other securities of a company whether constituting a charge on the assets of the company or not.” According to Topham, “Debenture is a document given by a company as evidence of a debt to the holder usually arising out of a loan and most commonly secured by a charge.”
Question 12.
What do you mean by redemption of debentures?
Answer:
Redemption of debentures means the repayment of the amount of debentures to debenture holders. In otherwords, redemption refers to discharge of liability on account of debentures by paying the due amount of debenture. The redemption of debentures is made by the company in accordance with the terms and conditions of issue which are clearly stated in the departure certificate.
Question 13.
Give the definition of financial statement analysis.
Answer:
According to finnery and miller, “Financial analysis consists in separating facts according to some definite plan, arranging then in group according to certain circumstances and then presenting them in a convenient and easily read and understandable form.”
According to John Myers “Financial statement analysis is largely a study of relationship among the various factors in a business as disclosed by a single set of statement and a study of the trends of these factors, as shown in a series of statements.”
Question 14.
What is ratio analysis?
Answer:
An analysis of financial statement with the help of ratio may be termed as ratio analysis. The ratio analysis is a very powerful analytical tool useful for measuring performance of a business enterprise. Thus, ratio analysis implies the process of computing, determining and presenting the relationship of items and groups of items in the financial statements.
Question 15.
What is current ratio or working capital ratio?
Answer:
Current ratio shows the relationship between current assets and current liabilities. It is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities on a particular date.
Current ratio =
Question 16.
What is quick ratio or liquid or acid test ratio?
Answer:
Quick ratio is the relationship between liquid assets and current liabilities. Quick ratio is computed by dividing liquid assets (or quick assets) by current liabilities.
Quick ratio or liquid ratio or acid test ratio =
Question 17.
What is the meaning of debt equity ratio?
Answer:
This ratio indicates die relationship between long term debt term debt and the equity (or shareholder’s funds). As such, this ratio is worked out by dividing long term debts by shareholder’s funds. It is usually expressed as a proportion.
Debt equity ratio =
Question 18.
What is total assets to debt ratio?
Answer:
This ratio shows the relationship between total assets and the long term debts of the business enterprise. It is usually expressed as pure ratio.
Total assets to debt ratio =
Question 19.
What is proprietary ratio?
Answer:
This ratio indicates the relationship between equity (or shareholder’s funds) and total assets and is computed by dividing the shareholder’s funds (equity) by total assets. It is usually expressed as a single ratio.
Proprietory ratio =
Question 20.
What is stock or inventory turnover ratio?
Answer:
This ratio shows the relationship between cost of goods sold during a given period and average stock carried during the period. Thus, stock turnover is obtained by dividing the cost of goods sold by average stock.
Stock turnover ratio =
Question 21.
What is working capital turnover ratio?
Answer:
This ratio shows the relationship between the net sales of the firm to its working capital. It is calculated by dividing net sales by working capital.
Working capital turnover ratio =
Question 22.
What is gross profit ratio?
Answer:
This ratio expresses the relationship between gross profit and sales. It is usually expressed in percentage.
Gross profit ratio =
Question 23.
What is operating ratio?
Answer:
This ratio expresses the relationship between cost of goods sold and operating expenses on the one hand and net sales on the other hand.
Operating ratio =
Question 24.
What is opening profit ratio?
Answer:
The operating profit ratio is calculated to establish relationship between operating profit and net sales. This ratio is also known as net operating ratio.
Operating profit ratio =
Question 25.
What is net profit ratio?
Answer:
This ratio relates to net profit to net sales. It is usually expressed as percentage.
Net Profit ratio =
Question 26.
What do you mean by cash flow statement?
Answer:
Cash flow statement deals with the preparation and presentation of statement of changes in cash flows during a particular period. In other words, it is a summary of source and application of cash during a particular span of time. Thus, it analyses the reasons for changes in balance of cash between two balance sheet dates.
Question 27.
Explain cash flow from operating activities.
Answer:
Operating activities are the main source of revenue and expenditure in an enterprise e.g., for a company manufacturing garments, purchase of raw material, payment of wages, sale of garments etc. therefore, they generally result from die transactions and other events that enter into the determination of net profit or net loss.
Question 28.
Explain cash flow front investing activities.
Answer:
Investing activities rotate to fixed assets, e.g., purchase and sale of land, building, computer, furniture, long term investment etc. As per As-3 investing activities are the acquisition and disposal of long term assets and other investments not included in cash equipments. Long term assets are there which are not kept for re-sale, e.g., building, furniture, machinery, plant etc.
Question 29.
Explain cash flow from financing activities.
Answer:
Financing activities are those which are related to long term equity and liabilities of an enterprise, i.e., cash receipts from issue of shares, debentures, raising long term loans and redemption of that loan etc. As per As-3, financing activities are activities than result in changes in the size and composition of the owner’s capital and borrowings of the enterprise.
Question 30.
Explain the limitations of cash flow statements.
Answer:
- Cash flow statement is only a supplementary statement and cannot replace the income statement.
- Cash flow statement cannot be equated with income statement.
- Cash flow statement ignores non-cash items.
- The cash balance as disclosed in the cash flow statement may not represent the real liquid position of the business.
Question 31.
Give three feature of Receipts and Payments Account.
Answer:
Features of Receipts and Payments Account:
- It is areal account.
- It is the summary of Cash and Bank transactions.
- All the receipts (whether they are of capital nature or revenue nature) are shown on the debit side of this account.
Question 32.
Distinguish between Income and Expenditure Account and Profit & Loss Account.
Answer:
Distinction between Income & Expenditure Account and Profit & Loss Account: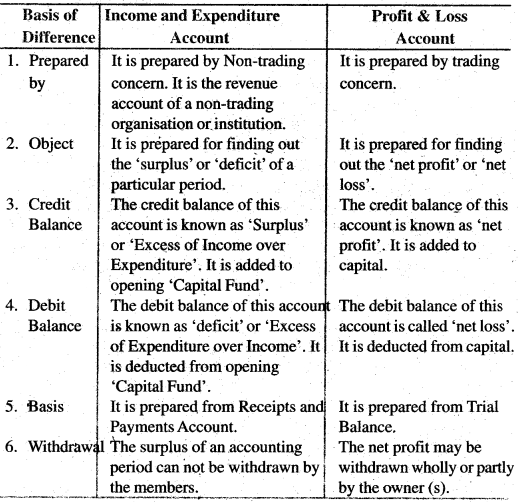
Question 33.
Difference between Receipts and Payment Account and Cash Book.
Answer:
Difference between Receipts and Payment Account and Cash Book: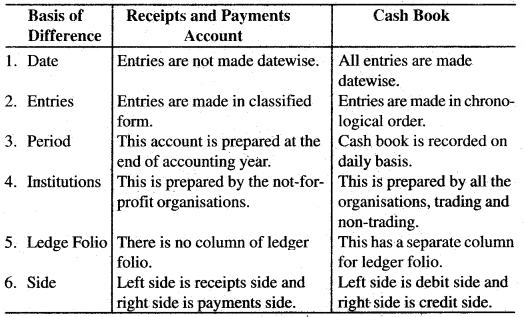
Question 34.
State six features of Income and Expenditure Account.
Answer:
Features of Income and Expenditure Account:
- It is a nominal account.
- It is prepared from the Receipts and Payments Account and other relevant information (or additional information).
- All revenue expenses related to current year are recorded on the debit side of the Income and expenditure account.
- All revenue incomes related to current year are shown on the credit side of Income and Expenditure Account.
- Items of capital nature are not shown in this account.
- It shows income and expenditure of current year only on accrual basis.
Question 35.
What is Receipts and Payments Account?
Answer:
Meaning of Receipts and Payments Account: A Receipts and Payments Account is a summary of cash receipts and cash payments relating to a given period. It is, in fact, a summary of the Cash Book. It is prepared at the end of the period under consideration. All receipts (relating to past, present or future period) are shown on the debit 6ide and all payments (relating to past, present or future) are shown on the credit side of this account.
It should be noted that in Receipts and Payments Account both revenue and capital items are shown. It does not give the date of transactions. Thus, both Cash Book and Receipts and Payments Account provide the same information but in different manner. Hence, in some respects they differ from each other.
